 Pipeline pigs are devices that are inserted into and travel throughout the
length of a pipeline driven by a product flow. They were originally developed to remove
deposits which could obstruct or retard flow through a pipeline. Today pigs are used
during all phases in the life of a pipeline for many different reasons.
Pipeline pigs are devices that are inserted into and travel throughout the
length of a pipeline driven by a product flow. They were originally developed to remove
deposits which could obstruct or retard flow through a pipeline. Today pigs are used
during all phases in the life of a pipeline for many different reasons.
Although each pipeline has its own set of characteristics which affect how and why pigging is used, there are basically three reasons to pig a pipeline:
- To batch or separate dissimilar products;
- For displacement purposes;
- For internal inspection.
The pigs which are used to accomplish these tasks can be divided into three categories:
- Utility Pigs, which are used to perform functions such as cleaning, separating, or dewatering.
- In Line Inspection Tools, which provide information on the condition of the line, as well as the extent and location of any problems.
- Gel Pigs, which are used in conjunction with conventional pigs to optimize pipeline dewatering, cleaning, and drying tasks.
The type of pig to be used and its optimum configuration for a particular task in a particular pipeline should be determined based upon several criteria, which include:
- The purpose
- Type, location, and volume of the substance to be removed or displaced in conventional pigging applications,
- Type of information to be gathered from an intelligent pig run,
- Objectives and goals for the pig run.

- The line contents
- The contents of the line while pigging,
- Available vs. required driving pressure,
- Velocity of the pig.
- Characteristics of the pipeline
- The minimum and maximum internal line sizes,
- Maximum distance pig must travel,
- Minimum bend radius, and bend angles,
- Additional features such as valve types, branch connections, and the elevation profile.

UTILITY PIGS

Utility pipeline pigs can be divided into two groups based upon their fundamental purpose:
- Cleaning Pigs, which are used to remove solid or semi-solid deposits or debris from the pipeline.
- Sealing Pigs, which are used to provide a good seal in order to either sweep liquids from the line, or provide an interface between two dissimilar products within the pipeline.
Within these two groups, a further subdivision can be made to differentiate among the various types or forms of pigs:
 • Mandrel pigs, which have a central body tube, or
mandrel, and various components which can be
assembled onto the mandrel to configure a pig for a specific duty;
• Mandrel pigs, which have a central body tube, or
mandrel, and various components which can be
assembled onto the mandrel to configure a pig for a specific duty;
 • Foam pigs, which are molded from polyurethane
foam with various configurations of solid polyurethane strips and/or abrasive materials
permanently bonded to them;
• Foam pigs, which are molded from polyurethane
foam with various configurations of solid polyurethane strips and/or abrasive materials
permanently bonded to them;
 • Solid cast pigs, which are moulded in one piece,
usually from polyurethane, and;
• Solid cast pigs, which are moulded in one piece,
usually from polyurethane, and;
 • Spherical pigs or spheres, which are of either a solid
composition or inflated to their optimum diameter with glycol and/or water.
• Spherical pigs or spheres, which are of either a solid
composition or inflated to their optimum diameter with glycol and/or water.
GEOMETRY PIGS

 A geometry / caliper pig is a configuration pig designed to record conditions, such as dents,
wrinkles, ovality, bend radius and angle, and occasionally indications of significant
internal corrosion by making measurements of the inside surface of the pipe.
A geometry / caliper pig is a configuration pig designed to record conditions, such as dents,
wrinkles, ovality, bend radius and angle, and occasionally indications of significant
internal corrosion by making measurements of the inside surface of the pipe.

IN LINE INSPECTION TOOLS (ILI) / SMART PIGS
 In Line Inspection provides information
on the condition of the pipe and/or its
contents. With few exceptions, the In
Line Inspection Tool itself is simply the
tool which gathers the data, which is then
analysed by the engineers and technicians
to determine and report on the condition
of the line.
In Line Inspection provides information
on the condition of the pipe and/or its
contents. With few exceptions, the In
Line Inspection Tool itself is simply the
tool which gathers the data, which is then
analysed by the engineers and technicians
to determine and report on the condition
of the line.


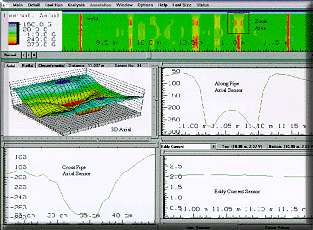
Although the two most common requirements are for geometry/diameter
 measurement and for metal-loss/corrosion devices, the information which can be provided by
these intelligent pigs covers a much wider range of inspection and troubleshooting needs
which include:
measurement and for metal-loss/corrosion devices, the information which can be provided by
these intelligent pigs covers a much wider range of inspection and troubleshooting needs
which include:
|

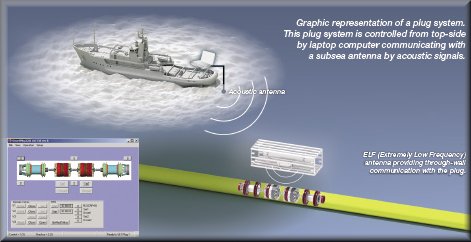
PLUGS
A plug is a specialist pig that can be used to isolate a section of pipeline at pressure while some remedial work is undertaken.
The plugs can withstand pressures up to 200 bars typically. The plug works by gripping into the line pipe and then having a separate sealing system. Lower pressure techniques include High Friction pigs, which provide a barrier for depressurised systems.

GEL PIGS
 Gel pigs are a series of gelled
liquid systems which have been developed for use in pipeline operations, either during
initial commissioning, or as a part of a continuing maintenance program. Most pipeline
gels are water-based, but a range of chemicals, solvents, and even acids can be gelled.
Some chemicals can be gelled as the bulk liquid and others only diluted in a carrier.
Gelled diesel is commonly used as a carrier of corrosion inhibitor in gas lines.
There are four main types of gel that are used in pipeline applications:
Gel pigs are a series of gelled
liquid systems which have been developed for use in pipeline operations, either during
initial commissioning, or as a part of a continuing maintenance program. Most pipeline
gels are water-based, but a range of chemicals, solvents, and even acids can be gelled.
Some chemicals can be gelled as the bulk liquid and others only diluted in a carrier.
Gelled diesel is commonly used as a carrier of corrosion inhibitor in gas lines.
There are four main types of gel that are used in pipeline applications:
- Batching, or separator gel
- Debris pickup gel
- Hydrocarbon gel
- Dehydrating gel
As a liquid, although highly viscous, the gel can be pumped through any line which will accept liquids. Gel pigs can be used alone (in liquid lines), in place of batching pigs, or in conjunction with various types of conventional pigs. When used with conventional pigs, gelled pigs can improve overall performance while almost eliminating the risk of sticking a pig.
Gel pigs do not wear out in service like conventional pigs. They can, however, be susceptible to dilution and gas cutting. Care must be taken, therefore, when designing a pig train that incorporates gel pigs to minimize fluid bypass of the pigs, and to place a conventional pig at the back of the train when displacing with gas.

The principle pipeline applications for gel pigs are as follows:
- Product separation
- Debris removal
- Line filling/hydrotesting
- Dewatering and drying
- Condensate removal from gas lines
- Inhibitor and biocide laydown
- Special chemical treatment
- Removal of stuck pigs
Specially formulated gels have also been used to seal valves during hydrostatic testing. Gels have been developed with a controlled gellation time and a controlled viscosity for temporary pipeline isolation purposes.
PIG TRAPS/LAUNCHERS/RECEIVERS
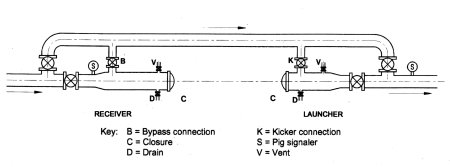 Pig traps are used for inserting pigs into a pipeline then
launching, receiving, and finally removing them without flow interruption. Pig traps are not generally
proprietary products and are usually made to a specification drawn up by the
user. However, pig trap closures are proprietary products and form a
critically important part of a pigging system. Safety is a major
consideration in the selection of a closure. All closures must have a
built-in safety lock which prevents them being opened while the trap is
pressurised.
Pig traps are used for inserting pigs into a pipeline then
launching, receiving, and finally removing them without flow interruption. Pig traps are not generally
proprietary products and are usually made to a specification drawn up by the
user. However, pig trap closures are proprietary products and form a
critically important part of a pigging system. Safety is a major
consideration in the selection of a closure. All closures must have a
built-in safety lock which prevents them being opened while the trap is
pressurised.

To learn more about pipeline pigging see PPSA Publication, "An Introduction to Pipeline Pigging."
